Why Are There So Many Pyramids?
Pyramids have fascinated humanity for centuries, standing as enigmatic and awe-inspiring structures that evoke curiosity and wonder.
These colossal monuments, most famously associated with ancient Egypt, have captured the collective imagination due to their sheer size, remarkable precision, and enduring presence.
However, what many people may not realize is that pyramids can be found in various corners of the world, stretching beyond the sands of Egypt.
This article delves into the fascinating question of why pyramids exist in diverse civilizations, exploring the historical, cultural, and technological factors that contributed to their construction.
Ancient Egypt: The Epitome of Pyramid Construction
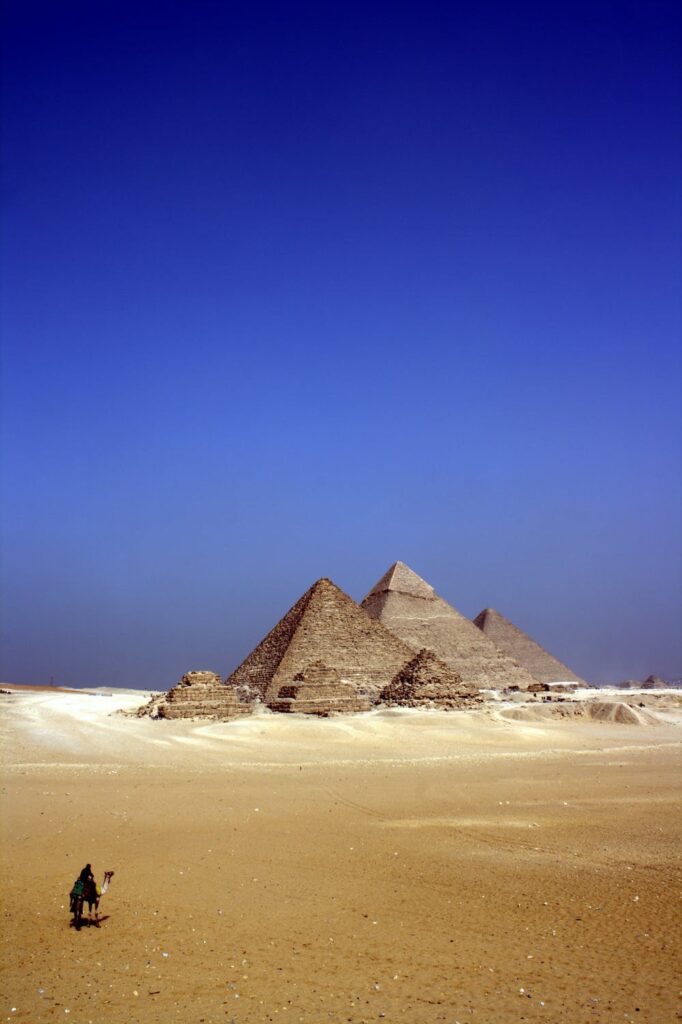
When discussing pyramids, it is impossible to overlook the monumental pyramids of ancient Egypt, such as the Great Pyramid of Giza.
The Egyptians built pyramids as tombs for their pharaohs, believing in the afterlife and the preservation of the ruler’s body for eternity.
The shape of the pyramid symbolized the sacred benben mound, a mythical creation place where the first rays of the sun illuminated the earth.
The Egyptians perfected the art of pyramid construction over centuries, culminating in the magnificent structures we see today.

Cultural Significance and Power Symbolism
Beyond Egypt, pyramids emerged in other ancient cultures, each with its own cultural and symbolic significance.
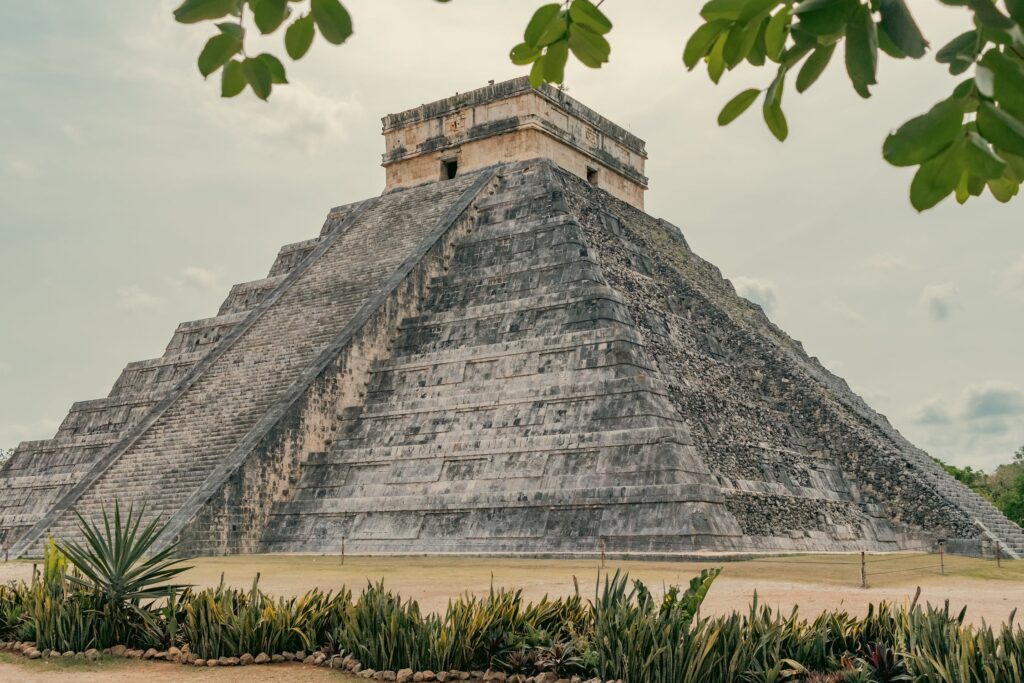
In Mesoamerica, the Maya, Aztecs, and other civilizations constructed pyramids as centers of religious and political power.
These towering structures served as sanctuaries, sacrificial altars, and platforms for astronomical observations.
The pyramids embodied the connection between the earthly and divine realms, symbolizing the aspirations of these civilizations to reach higher realms of knowledge and spiritual enlightenment.

Engineering Marvels and Technological Advances
The construction of pyramids required immense engineering prowess and sophisticated architectural techniques, a testament to the ingenuity of these ancient civilizations.
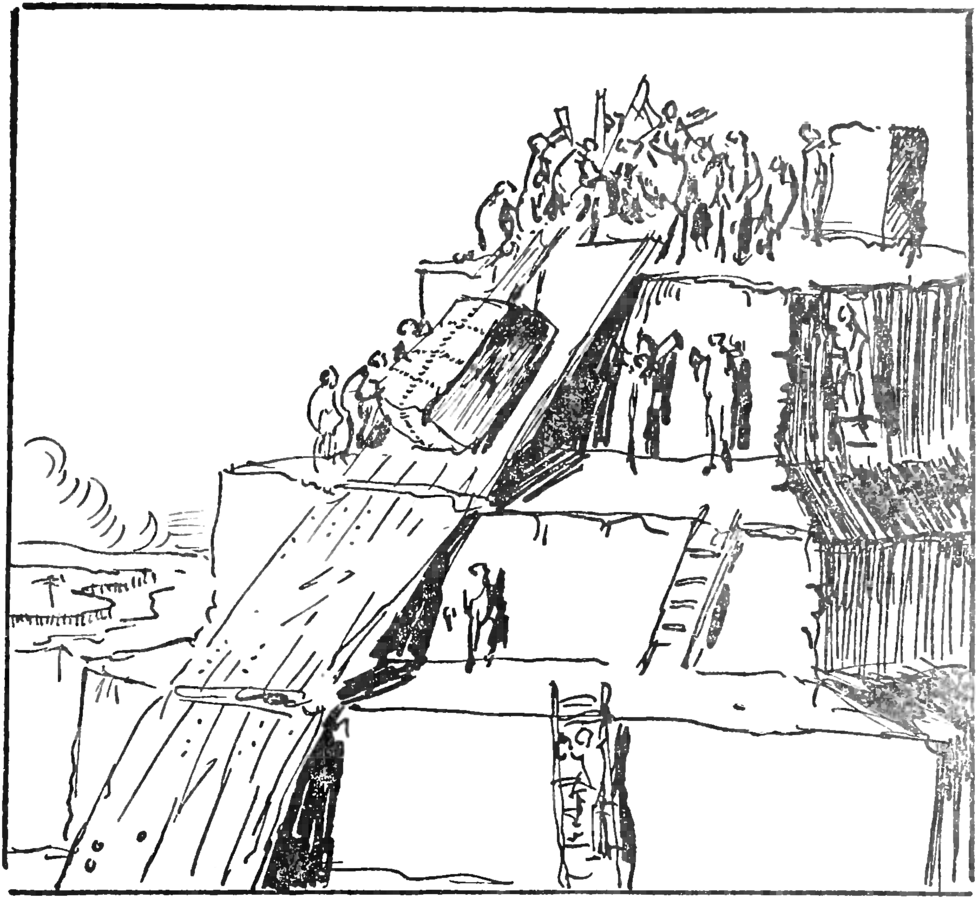
In ancient Egypt, the building process involved precise alignment with cardinal directions and careful arrangement of millions of stone blocks.
The Egyptians used inclined planes, ramps, and intricate pulley systems to transport and position the massive stones.
Similarly, in Mesoamerica, the Maya utilized advanced mathematics, astronomy, and engineering to create structurally sound pyramids with precise alignments to celestial events.
Sacred Geometry and Cosmic Alignment of Pyramids
The shape of pyramids embodies sacred geometry, reflecting a profound understanding of mathematics and cosmic alignment in various ancient cultures.
The sides of the Egyptian pyramids, for instance, form four equilateral triangles, representing the harmony and balance of the universe.
Moreover, the orientation of pyramids often aligned with celestial bodies or cardinal directions, revealing the connection between the earthly realm and the heavens.
These intentional alignments showcased the knowledge of astronomical phenomena and the belief in the interconnectedness of the cosmos.

Monumental Commemoration and Architectural Legacy
Pyramids were also constructed as lasting monuments to commemorate significant events or individuals.
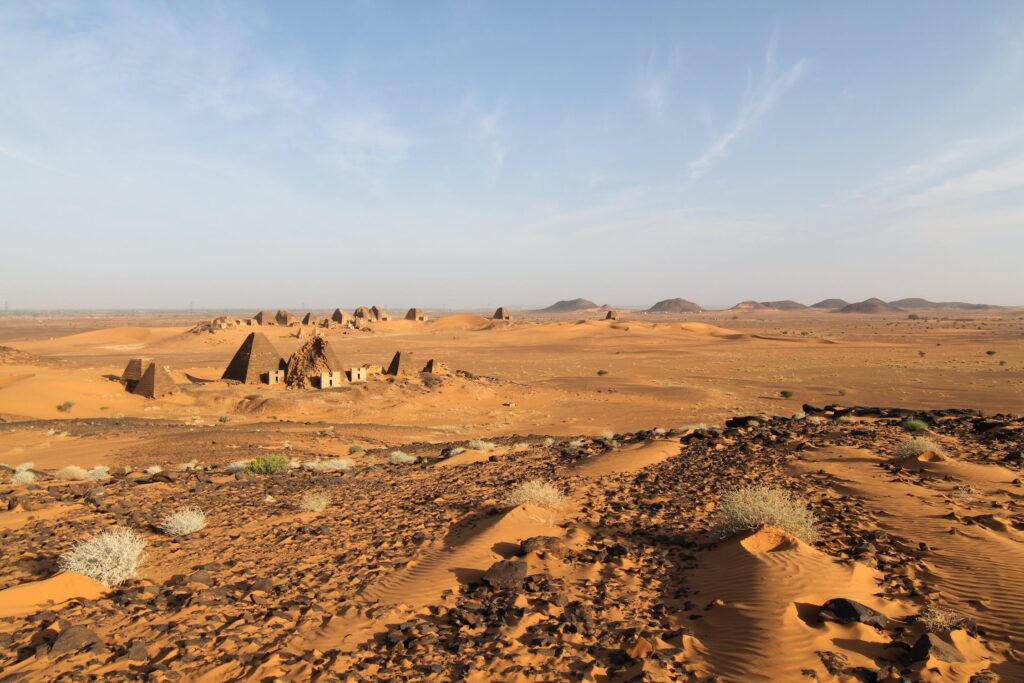
In ancient Nubia, the pyramids of Meroe were built to honor Nubian royalty and as burial places for the elite.
In China, the pyramidal-shaped mausoleums, such as the Maoling Mausoleum, served as burial sites for emperors of the Western Han Dynasty.
These structures not only preserved the memory of revered figures but also exemplified the architectural prowess of their respective civilizations, leaving behind an enduring legacy for future generations.

The existence of pyramids across various ancient civilizations can be attributed to a combination of cultural, symbolic, technological, and historical factors.
While ancient Egypt remains the pinnacle of pyramid construction, other cultures embraced the pyramid form for their own unique reasons.
Pyramids served as royal tombs, religious sanctuaries, power symbols, and astronomical observatories, reflecting the diverse aspirations and beliefs of the civilizations that built them.
The construction of pyramids showcased the extraordinary engineering capabilities of ancient societies, utilizing advanced techniques and technologies to create these monumental structures.
Moreover, the sacred geometry and intentional cosmic alignments embedded within pyramids revealed a deep understanding of the universe and its interconnectedness.
As we continue to study and explore these majestic pyramids, we unravel the rich tapestry of human history and the remarkable achievements of our ancestors.
The pyramids stand as enduring testaments to human ingenuity and as reminders of our eternal quest for knowledge, spirituality, and the pursuit of greatness.
Check out our other stuff
“Fun Fact: Did you know that the Great Pyramid of Giza, built around 4,500 years ago, was the tallest man-made structure in the world for over 3,800 years?
Standing at a staggering height of approximately 481 feet (147 meters), it remained unrivaled until the completion of the Lincoln Cathedral in England in 1311 AD.
This remarkable feat of engineering and architectural mastery showcases the awe-inspiring legacy of the ancient Egyptians and their enduring impact on human history.”
If you enjoyed this article, we invite you to explore our other captivating piece that delves into the intriguing question of why statues have proliferated throughout history.
Simply click the button below to embark on an engaging journey into the world of statues and uncover the fascinating stories behind their abundance.







