How Archaeologists Identify and Validate Archaeological Sites
Unveiling the Past
Archaeology is the scientific study of human history through the excavation and analysis of artifacts, structures, and other physical remains. Identifying and validating archaeological sites is a critical initial step in this investigative process. In this article, we will delve into the various methods and techniques that archaeologists employ to determine if a location holds historical significance and warrants further exploration.
Preliminary Research and Surveying
Before any shovels hit the ground, archaeologists conduct extensive preliminary research. They gather information from historical records, maps, and previous archaeological studies to identify potential sites. Satellite imagery and aerial photography are valuable tools in this phase, as they provide a bird’s-eye view of the landscape and can reveal irregularities that may indicate human activity from the past.

Ground Reconnaissance
Once potential sites are identified, archaeologists perform ground reconnaissance to survey the area in person. They walk the terrain, scanning for surface artifacts or features such as stone walls, pottery shards, or discolorations in the soil that may indicate buried structures. The presence of these indicators can validate a site’s potential and justify further investigation.

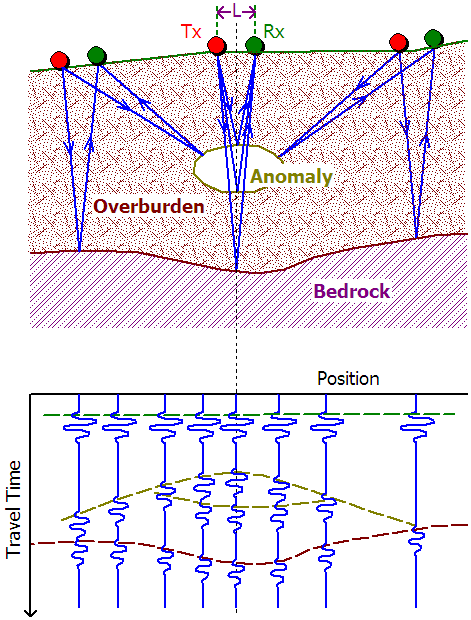
Geophysical Survey Techniques
Geophysical survey methods enable archaeologists to peer beneath the surface without excavation. Ground-penetrating radar, magnetometry, and resistivity surveys measure variations in the soil’s physical properties. This helps to identify buried walls, ditches, or other archaeological features. These non-invasive techniques are invaluable for creating a subsurface map of the site, guiding excavation efforts, and preserving the archaeological record.
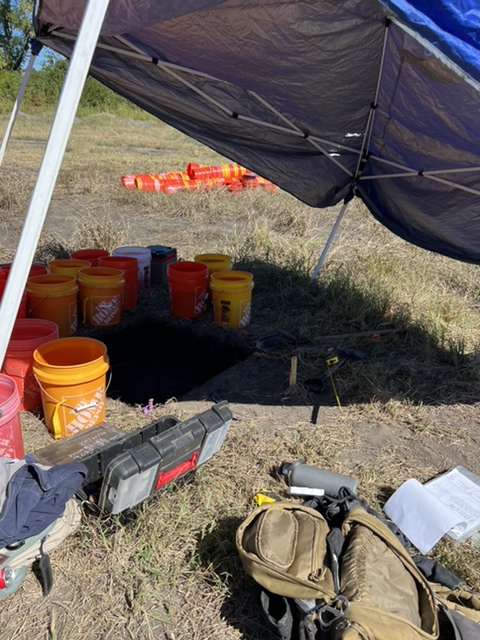
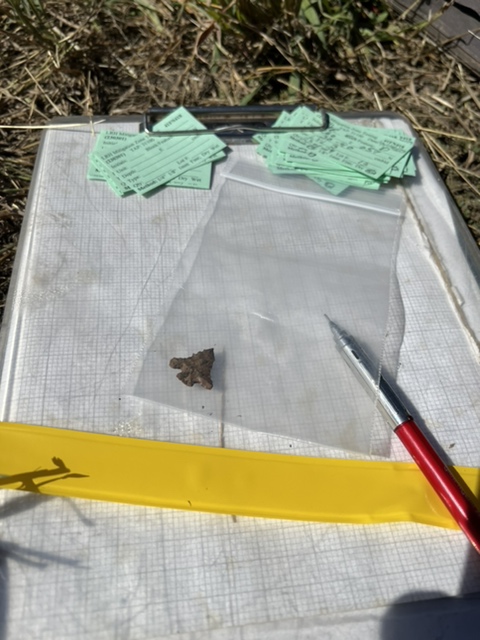
Test Excavations
When surface and geophysical surveys suggest a site’s potential, archaeologists may proceed with test excavations. These small, controlled digs help to confirm the presence of archaeological material and gather preliminary data on the site’s significance, age, and extent. The stratigraphy—or layering—of the soil is carefully analyzed, as different layers represent different periods of occupation or use.

Laboratory Analysis
Artifacts and samples collected from the site undergo rigorous laboratory analysis to provide further insights. Radiocarbon dating can determine the age of organic materials. Other techniques like dendrochronology (tree-ring dating) and thermoluminescence dating are used for specific types of artifacts or features. These analyses help archaeologists to construct a chronological framework for the site and interpret its historical context.

Ethnographic and Oral History
Engaging with local communities and indigenous peoples can provide valuable perspectives and information about a site. Oral histories and traditional knowledge can offer insights into the site’s significance, use, and meaning to different cultures, enriching the archaeological interpretation.

More info on archaeological sites
Determining if a location is an archaeological site is a meticulous and multifaceted process. Through a combination of preliminary research, ground reconnaissance, geophysical surveying, test excavations, laboratory analysis, and engagement with local communities, archaeologists can validate a site’s authenticity and unlock the secrets of the past.
By utilizing innovative techniques and respecting the voices of indigenous peoples, archaeology continues to evolve, ensuring that the discipline remains a vital tool in our quest to unravel the mysteries of our ancestors. Whether you are an aspiring archaeologist, a history enthusiast, or simply curious about the past, the fascinating world of archaeological discovery awaits, filled with intrigue, innovation, and the enduring allure of uncovering the unknown.
If you found this article insightful, explore real-life locations using our interactive map by clicking the button below.

“Did you know that some of the first aerial photographs used for archaeological purposes were taken from hot air balloons in the early 20th century? Pioneering archaeologists quickly realized the potential of getting a bird’s-eye view of landscapes to identify subtle variations in soil color, crop growth, and topography, which could reveal hidden archaeological sites. Today, we use advanced satellite imagery and aerial drones, but the principle remains the same. Sometimes the best way to uncover the secrets of the past is to take to the skies!”







