CRM vs. Academic Archaeology
Archaeology can be pursued through two distinct avenues: Cultural Resource Management (CRM) and Academic Archaeology.
While both fields share the common goal of unraveling the mysteries of the past, they diverge in their approaches and objectives.
In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of CRM and Academic Archaeology, exploring their similarities, differences, and the unique perspectives they bring to the table.
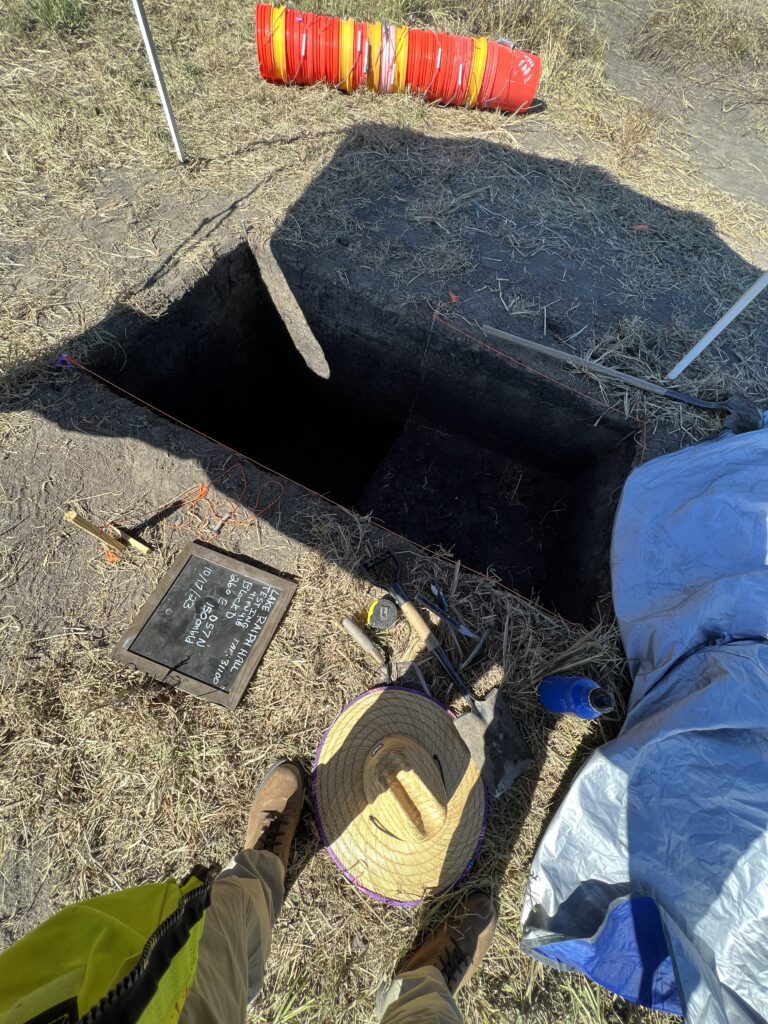
In the United States, most archaeologists are employed in the field of “Cultural Resource Management” (CRM). CRM is mandated by law and carried out by around 1,500 private archaeology companies. These companies conduct surveys and excavations to assess and protect cultural resources before construction projects.

The Significance of CRM
CRM is a field of archaeology that operates within the framework of regulatory compliance. Its primary aim is to identify, evaluate, and preserve cultural resources threatened by development projects.
As society advances, the need to strike a balance between progress and preserving our cultural heritage becomes increasingly vital.
CRM archaeologists work hand in hand with developers and regulatory bodies to conduct surveys, excavations, and documentation.
Their focus is often on the identification and management of archaeological sites, artifacts, and historical landscapes.
By examining these resources, CRM archaeologists provide crucial insights into the past while ensuring that valuable cultural heritage is protected for future generations.
If you’re interested in pursuing a career in CRM archaeology, I recommend checking out http://shovelbums.org/. It is the world’s largest provider of Archaeology, Academic, and Cultural Resource Management (CRM) related jobs.

Academic Archaeology: Uncovering the Past
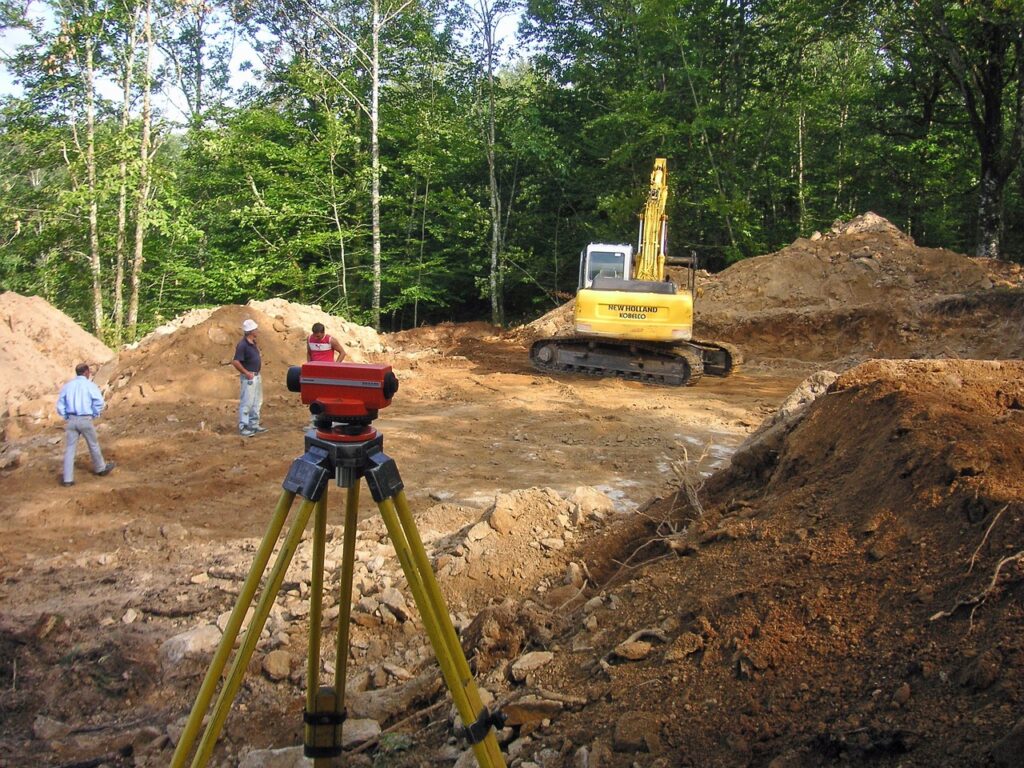
Academic Archaeology, in contrast, is primarily concerned with expanding knowledge and understanding through research and academic pursuits. These archaeologists are often associated with universities and research institutions.
They conduct excavations and fieldwork to answer fundamental questions about ancient civilizations, cultures, and the evolution of human societies.
Unlike CRM archaeologists who often work on specific projects with defined goals, academic archaeologists have the freedom to explore diverse research interests.
They may delve into topics such as ancient trade networks, ritual practices, or the origins of agriculture.
This pursuit of knowledge contributes to the broader academic discourse and advances our understanding of human history.
If you would like to learn more about this kind of archaeology, check out our other articles on the topic here: https://trowelandbrush.com/category/guide-to-archaeology/

The Synergy
While CRM and Academic Archaeology have distinct goals, they are not mutually exclusive. In fact, there is an inherent symbiotic relationship between the two, with each benefiting from the expertise and insights of the other.
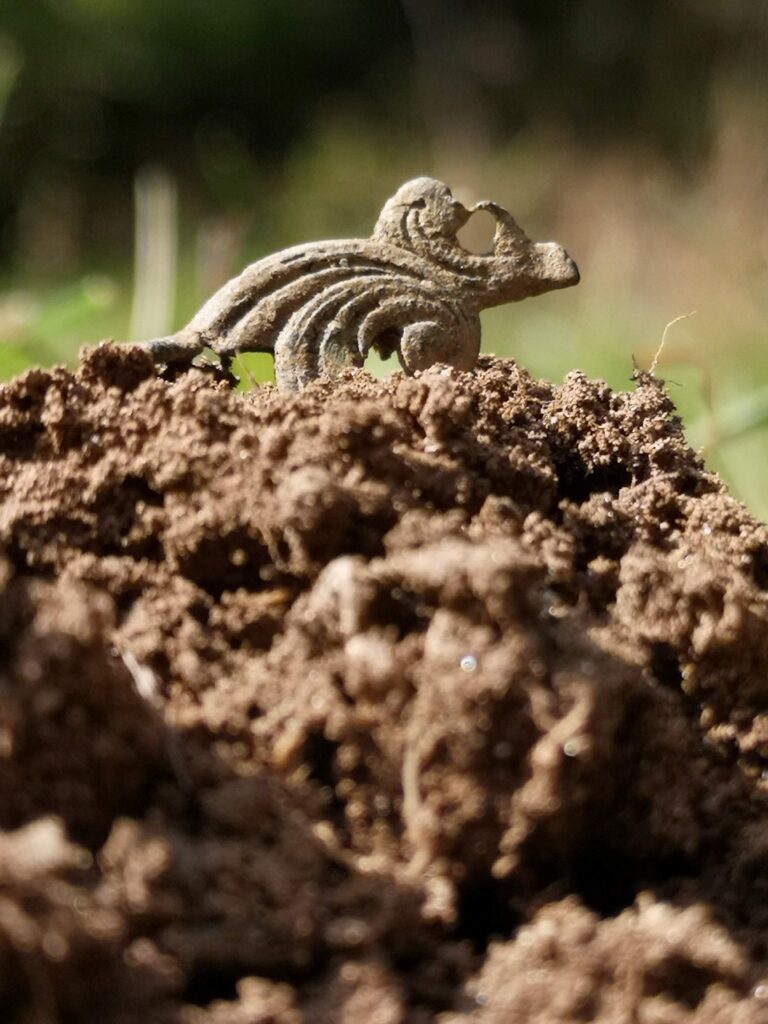
CRM archaeologists, for instance, contribute to academic research by providing data and resources.
Their work often generates new archaeological discoveries that shed light on previously unknown aspects of history.
Additionally, CRM projects serve as training grounds for emerging archaeologists, honing their skills and allowing them to contribute to the academic field in the future.
On the other hand, academic archaeologists play a vital role in contextualizing and interpreting the data collected by CRM archaeologists.
By applying rigorous research methodologies, they can provide a deeper understanding of the broader historical and cultural significance of the findings.
“CRM archaeologists often encounter unexpected connections between the past and the present. While excavating a site, they may come across artifacts or structures that have a direct link to the communities and individuals living in the area today.
These connections can be fascinating, as they provide tangible evidence of the continuity and resilience of human cultures over time.
It’s not uncommon for CRM archaeologists to engage with local communities, sharing their findings and collaborating on projects that honor and celebrate the shared heritage of the area.
This dynamic interaction between archaeologists and present-day communities adds a unique and enriching dimension to CRM archaeology, bridging the gap between past and present in meaningful ways.”
Conclusion
CRM and Academic Archaeology may have different priorities, but they are both crucial in the pursuit of knowledge about our past and the progress of society.
CRM not only safeguards cultural heritage but also contributes to academic research.
By conducting surveys, excavations, and documentation, CRM archaeologists generate valuable data and insights that contribute to the broader understanding of history.
These findings serve as building blocks for academic archaeologists who further contextualize and analyze them within a broader scholarly framework.
Through this collaboration, CRM and academic archaeology synergistically enhance our understanding of the past, illuminating the intricate layers of human history and cultural significance.
By recognizing the strengths and synergies between these fields, we can collectively unearth a more comprehensive narrative of our shared history.